메소드라고 부르고 이는 함수에 해당한다.
자바스크립트의 function, SQL에서 프로시저와 같은 기능을 한다.
메소드 이름
메소드 이름은 자바 식별자 규칙에 맞게 작성하여야 한다.
- 숫자로 시작할 수 없다.
- $와 _를 제외한 특수 문자를 사용하지 말아야 한다.
- 관례적으로 메소드 이름은 소문자로 작성한다.
- 서로 다른 단어가 혼합도니 이름이라면 뒤이어 오는 단어의 첫 글자는 대문자로 작성한다.
메소드 작성 영역
package oop0907;
public class Test01_method {
//메소드 작성 영역
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
메소드 구성
public static String test2(int a) {
if(a%2==0) {
return "짝수";
} else {
return "홀수";
}//if end
}//test2() end메소드 선언은 선언부와 실행 블록으로 구성된다. 선언부를 메소드 시그니처라고 부른다.
선언부에는 리턴 타입, 메소드 이름, 매개 변수 선언으로 이루어져 있다.
String이 리턴 타입, test2가 메소드 이름, (int a)가 매개 변수 선언에 해당한다.
만약 리턴 값이 없다면 void가 리턴 타입이다.
실행 블록은 { } 이다.
1. 리턴 값이 없는 함수
1) 전달값이 없는 경우
package oop0907;
public class Test01_method {
//메소드 작성 영역
//void는 리턴값이 없는 경우
public static void test1() {
System.out.println("JAVA");
}//test1() end
public static void test2() {
System.out.println("Python");
return; //함수는 호출한 시점으로 되돌아 간다
//마지막 return 명령어는 생략 가능하다
}//test2() end
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Method 메소드
// 함수, function, 프로시저
//1. 리턴값이 없는 함수
//1) 전달값(argument value)이 없는 경우
test1(); //함수 호출
test2();
test1();
}//main() end
}//class
2) 전달값이 있는 경우
package oop0907;
public class Test01_method {
//메소드 작성 영역
//void는 리턴값이 없는 경우
public static void test3(int a) { //매개변수(parameter)의 자료형은 생략 불가
System.out.println(a);
return;
}//test3() end
public static void test4(int a, int b, int c) { //매개변수는 자료형이 동일해도 각각 선언해야 함
System.out.println(a+b+c);
return;
}//test4() end
public static void test5(double a, double b) {
System.out.println(a+b);
return;
}//test5() end
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Method 메소드
// 함수, function, 프로시저
//1. 리턴값이 없는 함수
//2) 전달값이 있는 경우
test3(10);
test4(20, 30, 40);
test5(1.2, 3.4);
}//main() end
}//class end
연습문제
//문제) #기호를 100번 출력하시오
byte num=100; //byte : -128 ~ +127
char ch='#';
test6(ch, num);public static void test6(char c, byte n) {
for(int a=1; a<+n; a++) {
System.out.print(c);
}//for end
}//test6() end
2. 리턴 값이 있는 함수
package oop0907;
public class Test02_method {
public static int test1(int a, int b) {
int c = a+b;
//return; 리턴값이 없다 (void). 리턴값은 1개 값만 할 수 있다
return c; //리턴값이 있는 경우 리턴값의 자료형을 void 자리에 쓴다
}//test1() end
public static String test2(int a) {
if(a%2==0) {
return "짝수";
} else {
return "홀수";
}//if end
}//test2() end
public static boolean test3(int y) {
if (y%4==0 && y%100!=0 || y%400==0) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}//if end
}//test3() end
public static long test4(int n) {
long gop=1;
for(int a=n; a>0; a--) {
gop *= a;
}//for end
return gop;
}//test4() end
public static long fact(int n) { //재귀적 함수 호출
if(n==0) {
return 1;
} else {
return n*fact(n-1);
}//if end
}//fact() end
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 2. 리턴값이 있는 경우
// 예) Math
// System.out.println(Math.abs(-3));
// System.out.println(Math.max(5, 7));
int result = test1(2, 4);
System.out.println(result);
//값 : 상수값, 변수값, 리턴값
System.out.println(test1(5,6));
//짝수, 홀수 출력하기
String str=test2(7);
System.out.println(str);
//윤년 확인하기
if(test3(2022)) {
System.out.println("윤년");
} else {
System.out.println("평년");
}//if end
//팩토리얼 구하기
long f=test4(5);
System.out.println(f);
//////////////////////////////////
//3. 재귀적 함수 호출
//팩토리얼값 구하기
System.out.println(fact(5));
}//main() end
}//class end
함수 호출 방식

- Call by value : 값에 의한 호출 방식
- Call by reference : 주소에 의한 호출 방식
int[] num= {10, 20 ,30};
//Call by value
test1(num[0], num[2]); //10, 30
//Call by reference
test2(num); //배열 요소가 저장되어 있는 주소. 배열 전체package oop0907;
public class Test05_method {
public static void test1(int a, int b) {
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
}//test1() end
public static void test2(int[] a) {
for(int i=0; i<a.length; i++) {
System.out.println(a[i]);
}
}//test2() end
public static void test3(String a, String b) {
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
}//test3() end
public static void test4(String[] a) {
for(int i=0; i<a.length; i++) {
System.out.println(a[i]);
}//for end
}//test4() end
public static void test5(int a, int b) {
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
}//test5() end
public static void test6(int[][] a) {
for(int i=0; i<a.length; i++) {
int col=a[i].length;
for(int j=0; j<col; j++) {
System.out.println(a[i][j]);
}//for end
}//for end
}//test6() end
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 함수 호출 방식
//-> Call by value 값에 의한 호출 방식
//-> Call by reference 주소에 의한 호출 방식
int[] num= {10, 20 ,30};
//Call by value
test1(num[0], num[2]); //10, 30
//Call by reference
test2(num); //배열 요소가 저장되어 있는 주소. 배열 전체
String[] name= {"무궁화", "진달래", "개나리"};
test3(name[0], name[2]); //무궁화, 개나리
test4(name);
int[][] su = { {1, 2, 3}
, {4, 5, 6}
}; //2행 3열
test5(su[0][0], su[1][1]); //1, 5
test6(su);
}//main() end
}//class end
int[] lotto = {3, 7, 4, 15, 28, 13};
Arrays.sort(lotto); //1차원 배열을 전달하면 오름차순 정렬
for(int i=0; i<lotto.length; i++) {
System.out.println(lotto[i]);
}//for end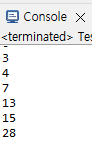
'웹개발 교육 > Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [31일] Java (17) - 연습 문제 (0) | 2022.09.07 |
|---|---|
| [31일] Java (16) - Overload (0) | 2022.09.07 |
| [30 ~ 31일] Java (14) - 정렬 (0) | 2022.09.06 |
| [30일] Java (13) - 배열 연습문제 (0) | 2022.09.06 |
| [30일] Java (12) - 배열 (0) | 2022.09.06 |
메소드라고 부르고 이는 함수에 해당한다.
자바스크립트의 function, SQL에서 프로시저와 같은 기능을 한다.
메소드 이름
메소드 이름은 자바 식별자 규칙에 맞게 작성하여야 한다.
- 숫자로 시작할 수 없다.
- $와 _를 제외한 특수 문자를 사용하지 말아야 한다.
- 관례적으로 메소드 이름은 소문자로 작성한다.
- 서로 다른 단어가 혼합도니 이름이라면 뒤이어 오는 단어의 첫 글자는 대문자로 작성한다.
메소드 작성 영역
package oop0907;
public class Test01_method {
//메소드 작성 영역
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
메소드 구성
public static String test2(int a) {
if(a%2==0) {
return "짝수";
} else {
return "홀수";
}//if end
}//test2() end메소드 선언은 선언부와 실행 블록으로 구성된다. 선언부를 메소드 시그니처라고 부른다.
선언부에는 리턴 타입, 메소드 이름, 매개 변수 선언으로 이루어져 있다.
String이 리턴 타입, test2가 메소드 이름, (int a)가 매개 변수 선언에 해당한다.
만약 리턴 값이 없다면 void가 리턴 타입이다.
실행 블록은 { } 이다.
1. 리턴 값이 없는 함수
1) 전달값이 없는 경우
package oop0907;
public class Test01_method {
//메소드 작성 영역
//void는 리턴값이 없는 경우
public static void test1() {
System.out.println("JAVA");
}//test1() end
public static void test2() {
System.out.println("Python");
return; //함수는 호출한 시점으로 되돌아 간다
//마지막 return 명령어는 생략 가능하다
}//test2() end
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Method 메소드
// 함수, function, 프로시저
//1. 리턴값이 없는 함수
//1) 전달값(argument value)이 없는 경우
test1(); //함수 호출
test2();
test1();
}//main() end
}//class
2) 전달값이 있는 경우
package oop0907;
public class Test01_method {
//메소드 작성 영역
//void는 리턴값이 없는 경우
public static void test3(int a) { //매개변수(parameter)의 자료형은 생략 불가
System.out.println(a);
return;
}//test3() end
public static void test4(int a, int b, int c) { //매개변수는 자료형이 동일해도 각각 선언해야 함
System.out.println(a+b+c);
return;
}//test4() end
public static void test5(double a, double b) {
System.out.println(a+b);
return;
}//test5() end
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Method 메소드
// 함수, function, 프로시저
//1. 리턴값이 없는 함수
//2) 전달값이 있는 경우
test3(10);
test4(20, 30, 40);
test5(1.2, 3.4);
}//main() end
}//class end
연습문제
//문제) #기호를 100번 출력하시오
byte num=100; //byte : -128 ~ +127
char ch='#';
test6(ch, num);public static void test6(char c, byte n) {
for(int a=1; a<+n; a++) {
System.out.print(c);
}//for end
}//test6() end
2. 리턴 값이 있는 함수
package oop0907;
public class Test02_method {
public static int test1(int a, int b) {
int c = a+b;
//return; 리턴값이 없다 (void). 리턴값은 1개 값만 할 수 있다
return c; //리턴값이 있는 경우 리턴값의 자료형을 void 자리에 쓴다
}//test1() end
public static String test2(int a) {
if(a%2==0) {
return "짝수";
} else {
return "홀수";
}//if end
}//test2() end
public static boolean test3(int y) {
if (y%4==0 && y%100!=0 || y%400==0) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}//if end
}//test3() end
public static long test4(int n) {
long gop=1;
for(int a=n; a>0; a--) {
gop *= a;
}//for end
return gop;
}//test4() end
public static long fact(int n) { //재귀적 함수 호출
if(n==0) {
return 1;
} else {
return n*fact(n-1);
}//if end
}//fact() end
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 2. 리턴값이 있는 경우
// 예) Math
// System.out.println(Math.abs(-3));
// System.out.println(Math.max(5, 7));
int result = test1(2, 4);
System.out.println(result);
//값 : 상수값, 변수값, 리턴값
System.out.println(test1(5,6));
//짝수, 홀수 출력하기
String str=test2(7);
System.out.println(str);
//윤년 확인하기
if(test3(2022)) {
System.out.println("윤년");
} else {
System.out.println("평년");
}//if end
//팩토리얼 구하기
long f=test4(5);
System.out.println(f);
//////////////////////////////////
//3. 재귀적 함수 호출
//팩토리얼값 구하기
System.out.println(fact(5));
}//main() end
}//class end
함수 호출 방식

- Call by value : 값에 의한 호출 방식
- Call by reference : 주소에 의한 호출 방식
int[] num= {10, 20 ,30};
//Call by value
test1(num[0], num[2]); //10, 30
//Call by reference
test2(num); //배열 요소가 저장되어 있는 주소. 배열 전체package oop0907;
public class Test05_method {
public static void test1(int a, int b) {
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
}//test1() end
public static void test2(int[] a) {
for(int i=0; i<a.length; i++) {
System.out.println(a[i]);
}
}//test2() end
public static void test3(String a, String b) {
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
}//test3() end
public static void test4(String[] a) {
for(int i=0; i<a.length; i++) {
System.out.println(a[i]);
}//for end
}//test4() end
public static void test5(int a, int b) {
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
}//test5() end
public static void test6(int[][] a) {
for(int i=0; i<a.length; i++) {
int col=a[i].length;
for(int j=0; j<col; j++) {
System.out.println(a[i][j]);
}//for end
}//for end
}//test6() end
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 함수 호출 방식
//-> Call by value 값에 의한 호출 방식
//-> Call by reference 주소에 의한 호출 방식
int[] num= {10, 20 ,30};
//Call by value
test1(num[0], num[2]); //10, 30
//Call by reference
test2(num); //배열 요소가 저장되어 있는 주소. 배열 전체
String[] name= {"무궁화", "진달래", "개나리"};
test3(name[0], name[2]); //무궁화, 개나리
test4(name);
int[][] su = { {1, 2, 3}
, {4, 5, 6}
}; //2행 3열
test5(su[0][0], su[1][1]); //1, 5
test6(su);
}//main() end
}//class end
int[] lotto = {3, 7, 4, 15, 28, 13};
Arrays.sort(lotto); //1차원 배열을 전달하면 오름차순 정렬
for(int i=0; i<lotto.length; i++) {
System.out.println(lotto[i]);
}//for end
'웹개발 교육 > Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [31일] Java (17) - 연습 문제 (0) | 2022.09.07 |
|---|---|
| [31일] Java (16) - Overload (0) | 2022.09.07 |
| [30 ~ 31일] Java (14) - 정렬 (0) | 2022.09.06 |
| [30일] Java (13) - 배열 연습문제 (0) | 2022.09.06 |
| [30일] Java (12) - 배열 (0) | 2022.09.06 |
