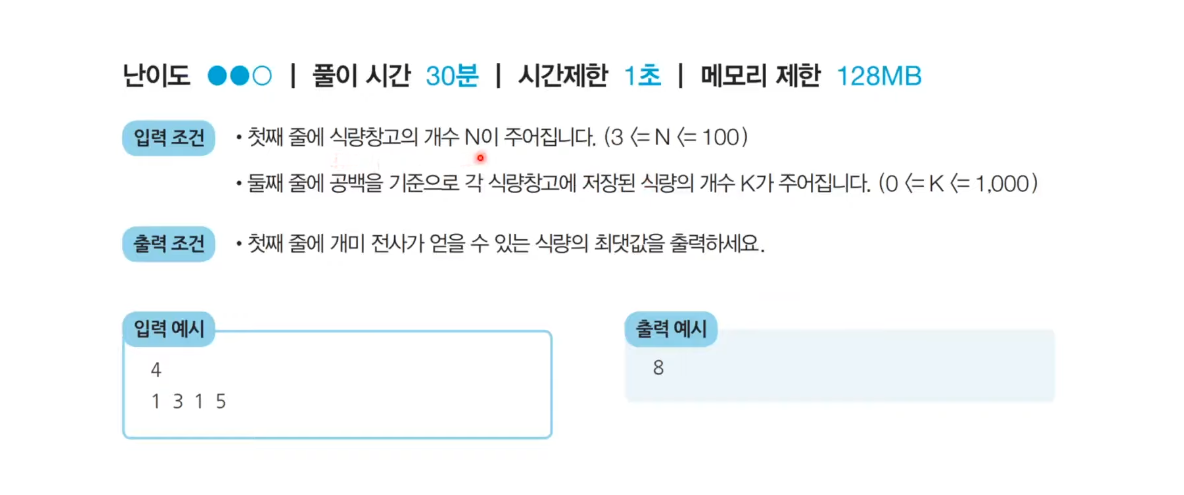
문제 1






더보기
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
// 앞서 계산된 결과를 저장하기 위한 DP 테이블 초기화
public static int[] d = new int[100];
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// 정수 N을 입력받기
int n = sc.nextInt();
// 모든 식량 정보 입력받기
int[] arr = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
// 다이나믹 프로그래밍(Dynamic Programming) 진행(보텀업)
d[0] = arr[0];
d[1] = Math.max(arr[0], arr[1]);
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) {
d[i] = Math.max(d[i - 1], d[i - 2] + arr[i]);
}
// 계산된 결과 출력
System.out.println(d[n - 1]);
}
}
문제 2




더보기
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
// 앞서 계산된 결과를 저장하기 위한 DP 테이블 초기화
public static int[] d = new int[30001];
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int x = sc.nextInt();
// 다이나믹 프로그래밍(Dynamic Programming) 진행(보텀업)
for (int i = 2; i <= x; i++) {
// 현재의 수에서 1을 빼는 경우
d[i] = d[i - 1] + 1;
// 현재의 수가 2로 나누어 떨어지는 경우
if (i % 2 == 0)
d[i] = Math.min(d[i], d[i / 2] + 1);
// 현재의 수가 3으로 나누어 떨어지는 경우
if (i % 3 == 0)
d[i] = Math.min(d[i], d[i / 3] + 1);
// 현재의 수가 5로 나누어 떨어지는 경우
if (i % 5 == 0)
d[i] = Math.min(d[i], d[i / 5] + 1);
}
System.out.println(d[x]);
}
}
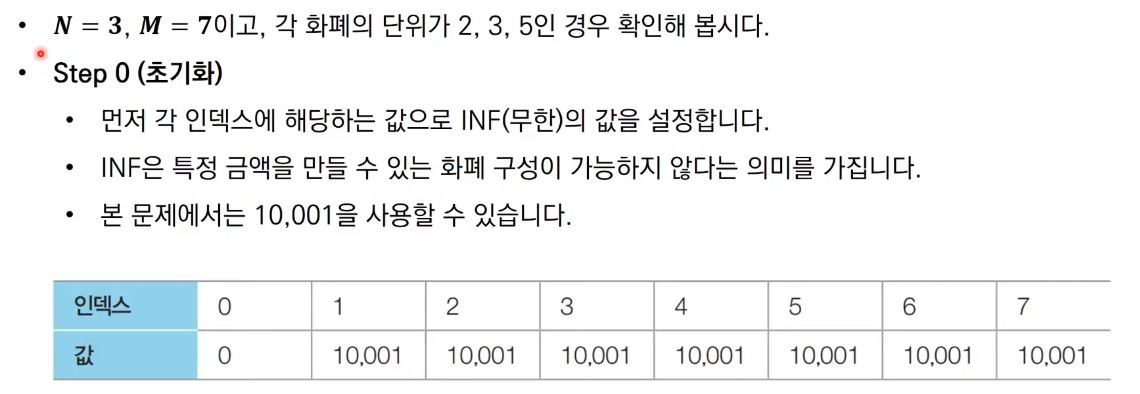
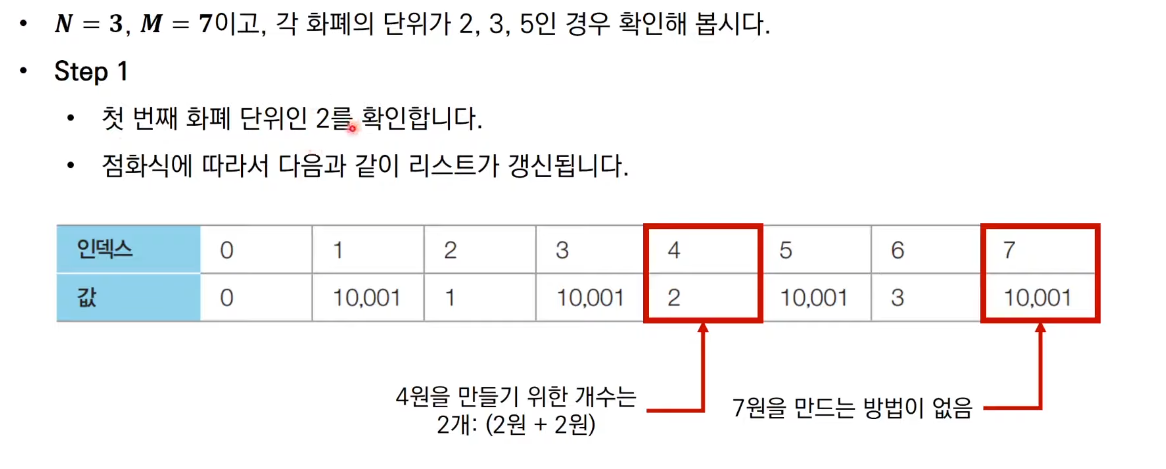
문제 3





더보기
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// 정수 N, M을 입력받기
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
// N개의 화폐 단위 정보를 입력 받기
int[] arr = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
// 앞서 계산된 결과를 저장하기 위한 DP 테이블 초기화
int[] d = new int[m + 1];
Arrays.fill(d, 10001);
// 다이나믹 프로그래밍(Dynamic Programming) 진행(보텀업)
d[0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = arr[i]; j <= m; j++) {
// (i - k)원을 만드는 방법이 존재하는 경우
if (d[j - arr[i]] != 10001) {
d[j] = Math.min(d[j], d[j - arr[i]] + 1);
}
}
}
// 계산된 결과 출력
if (d[m] == 10001) { // 최종적으로 M원을 만드는 방법이 없는 경우
System.out.println(-1);
}
else {
System.out.println(d[m]);
}
}
}
문제 4





더보기
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static int testCase, n, m;
static int[][] arr = new int[20][20];
static int[][] dp = new int[20][20];
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// 테스트 케이스(Test Case) 입력
testCase = sc.nextInt();
for (int tc = 0; tc < testCase; tc++) {
// 금광 정보 입력
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
arr[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
// 다이나믹 프로그래밍을 위한 2차원 DP 테이블 초기화
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
dp[i][j] = arr[i][j];
}
}
// 다이나믹 프로그래밍 진행
for (int j = 1; j < m; j++) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int leftUp, leftDown, left;
// 왼쪽 위에서 오는 경우
if (i == 0) leftUp = 0;
else leftUp = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
// 왼쪽 아래에서 오는 경우
if (i == n - 1) leftDown = 0;
else leftDown = dp[i + 1][j - 1];
// 왼쪽에서 오는 경우
left = dp[i][j - 1];
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j] + Math.max(leftUp, Math.max(leftDown, left));
}
}
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
result = Math.max(result, dp[i][m - 1]);
}
System.out.println(result);
}
}
}
문제 5








4와 비교했을 때 5가 더큼. 2와 비교했을 때도 5가 더 크다. 그런데 이미 4와 비교했을 때 1을 더했으니 2와 비교했을 때는 1을 더할 필요 없다. 4를 제거하면 {2,5}, 2를 제거하면 {4,5}이므로 증가하는 부분 수열이다.


더보기
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static int n;
static ArrayList<Integer> v = new ArrayList<Integer>();
static int[] dp = new int[2000];
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
v.add(sc.nextInt());
}
// 순서를 뒤집어 '최장 증가 부분 수열' 문제로 변환
Collections.reverse(v);
// 다이나믹 프로그래밍을 위한 1차원 DP 테이블 초기화
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
dp[i] = 1;
}
// 가장 긴 증가하는 부분 수열(LIS) 알고리즘 수행
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (v.get(j) < v.get(i)) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1);
}
}
}
// 열외해야 하는 병사의 최소 수를 출력
int maxValue = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
maxValue = Math.max(maxValue, dp[i]);
}
System.out.println(n - maxValue);
}
}
'알고리즘 > 정리' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 다이나믹 프로그래밍 (0) | 2023.03.16 |
|---|---|
| 이진 탐색 유형 문제 (0) | 2023.03.13 |
| 이진 탐색 (0) | 2023.03.13 |
| 그래프 탐색 알고리즘(DFS/BFS) 유형 문제 (0) | 2023.03.13 |
| 그래프 탐색 알고리즘(DFS/BFS)(4) - BFS(Breadth-First Search) (0) | 2023.03.13 |
문제 1







더보기
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
// 앞서 계산된 결과를 저장하기 위한 DP 테이블 초기화
public static int[] d = new int[100];
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// 정수 N을 입력받기
int n = sc.nextInt();
// 모든 식량 정보 입력받기
int[] arr = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
// 다이나믹 프로그래밍(Dynamic Programming) 진행(보텀업)
d[0] = arr[0];
d[1] = Math.max(arr[0], arr[1]);
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) {
d[i] = Math.max(d[i - 1], d[i - 2] + arr[i]);
}
// 계산된 결과 출력
System.out.println(d[n - 1]);
}
}
문제 2




더보기
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
// 앞서 계산된 결과를 저장하기 위한 DP 테이블 초기화
public static int[] d = new int[30001];
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int x = sc.nextInt();
// 다이나믹 프로그래밍(Dynamic Programming) 진행(보텀업)
for (int i = 2; i <= x; i++) {
// 현재의 수에서 1을 빼는 경우
d[i] = d[i - 1] + 1;
// 현재의 수가 2로 나누어 떨어지는 경우
if (i % 2 == 0)
d[i] = Math.min(d[i], d[i / 2] + 1);
// 현재의 수가 3으로 나누어 떨어지는 경우
if (i % 3 == 0)
d[i] = Math.min(d[i], d[i / 3] + 1);
// 현재의 수가 5로 나누어 떨어지는 경우
if (i % 5 == 0)
d[i] = Math.min(d[i], d[i / 5] + 1);
}
System.out.println(d[x]);
}
}
문제 3







더보기
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// 정수 N, M을 입력받기
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
// N개의 화폐 단위 정보를 입력 받기
int[] arr = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
// 앞서 계산된 결과를 저장하기 위한 DP 테이블 초기화
int[] d = new int[m + 1];
Arrays.fill(d, 10001);
// 다이나믹 프로그래밍(Dynamic Programming) 진행(보텀업)
d[0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = arr[i]; j <= m; j++) {
// (i - k)원을 만드는 방법이 존재하는 경우
if (d[j - arr[i]] != 10001) {
d[j] = Math.min(d[j], d[j - arr[i]] + 1);
}
}
}
// 계산된 결과 출력
if (d[m] == 10001) { // 최종적으로 M원을 만드는 방법이 없는 경우
System.out.println(-1);
}
else {
System.out.println(d[m]);
}
}
}
문제 4





더보기
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static int testCase, n, m;
static int[][] arr = new int[20][20];
static int[][] dp = new int[20][20];
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// 테스트 케이스(Test Case) 입력
testCase = sc.nextInt();
for (int tc = 0; tc < testCase; tc++) {
// 금광 정보 입력
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
arr[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
// 다이나믹 프로그래밍을 위한 2차원 DP 테이블 초기화
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
dp[i][j] = arr[i][j];
}
}
// 다이나믹 프로그래밍 진행
for (int j = 1; j < m; j++) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int leftUp, leftDown, left;
// 왼쪽 위에서 오는 경우
if (i == 0) leftUp = 0;
else leftUp = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
// 왼쪽 아래에서 오는 경우
if (i == n - 1) leftDown = 0;
else leftDown = dp[i + 1][j - 1];
// 왼쪽에서 오는 경우
left = dp[i][j - 1];
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j] + Math.max(leftUp, Math.max(leftDown, left));
}
}
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
result = Math.max(result, dp[i][m - 1]);
}
System.out.println(result);
}
}
}
문제 5








4와 비교했을 때 5가 더큼. 2와 비교했을 때도 5가 더 크다. 그런데 이미 4와 비교했을 때 1을 더했으니 2와 비교했을 때는 1을 더할 필요 없다. 4를 제거하면 {2,5}, 2를 제거하면 {4,5}이므로 증가하는 부분 수열이다.


더보기
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static int n;
static ArrayList<Integer> v = new ArrayList<Integer>();
static int[] dp = new int[2000];
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
v.add(sc.nextInt());
}
// 순서를 뒤집어 '최장 증가 부분 수열' 문제로 변환
Collections.reverse(v);
// 다이나믹 프로그래밍을 위한 1차원 DP 테이블 초기화
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
dp[i] = 1;
}
// 가장 긴 증가하는 부분 수열(LIS) 알고리즘 수행
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (v.get(j) < v.get(i)) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1);
}
}
}
// 열외해야 하는 병사의 최소 수를 출력
int maxValue = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
maxValue = Math.max(maxValue, dp[i]);
}
System.out.println(n - maxValue);
}
}
'알고리즘 > 정리' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 다이나믹 프로그래밍 (0) | 2023.03.16 |
|---|---|
| 이진 탐색 유형 문제 (0) | 2023.03.13 |
| 이진 탐색 (0) | 2023.03.13 |
| 그래프 탐색 알고리즘(DFS/BFS) 유형 문제 (0) | 2023.03.13 |
| 그래프 탐색 알고리즘(DFS/BFS)(4) - BFS(Breadth-First Search) (0) | 2023.03.13 |
